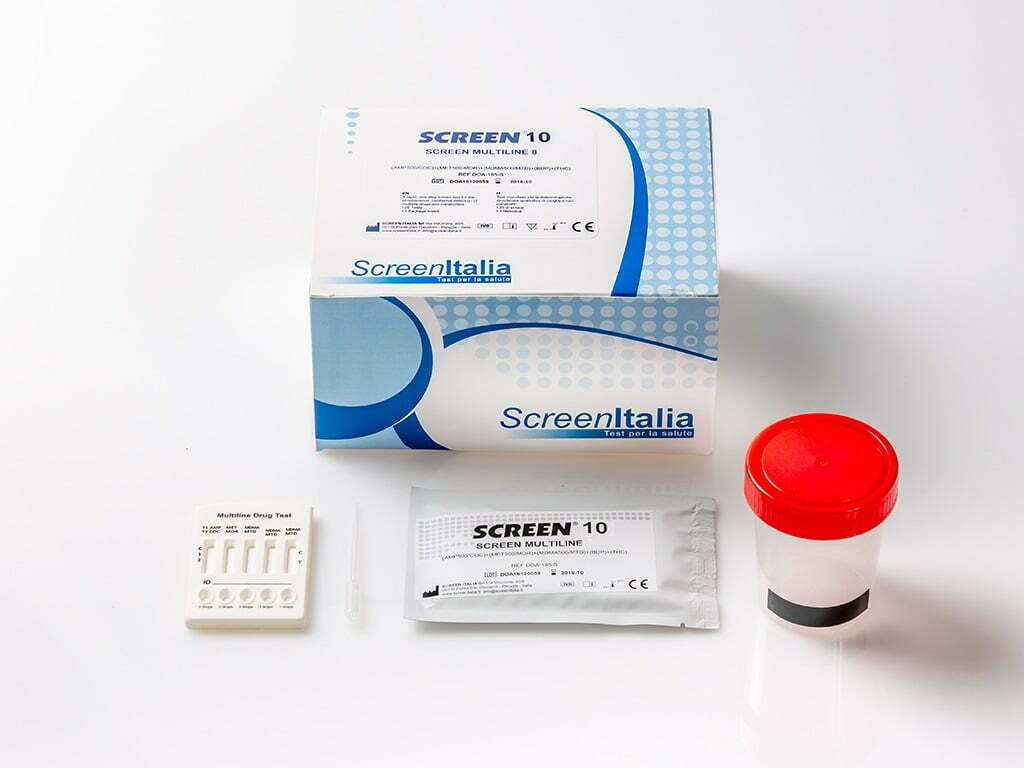
Adulteration Urine Test
The Urine Adulteration Dipsticks (Urine) are a semi-quantitative color comparison screen for the detection of Creatinine, Nitrite, Glutaraldehyde, pH, Specific Gravity, Oxidants and Pyridinium Chlorochromate in human urine
Description
Product information
The Urine Adulteration Dipsticks (Urine) are a semi-quantitative color comparison screen for the detection of Creatinine, Nitrite, Glutaraldehyde, pH, Specific Gravity, Oxidants and Pyridinium Chlorochromate in human urine.
Advantages of Adulteration test
- Easy to perform
- No limit to sample volume
- No drug rapid tests is wasted
- Low cost given the advantages it offers
General information
Adulteration is the tampering of a urine specimen with the intention of altering the test results. The use of adulterants can cause false negative results in drug tests by either interfering with the screening test and/or destroying the drugs present in the urine. Dilution may also be employed in an attempt to produce false negative drug test results. One of the best ways to test for adulteration or dilution is to determine certain urinary characteristics such as Creatinine, pH, and Specific Gravity and to detect the presence of Glutaraldehyde, Nitrite and Oxidants/Pyridinium Chlorochromate in urine.
- Creatinine (CRE) tests for specimen dilution. Creatinine is a waste product of Creatine, and is an amino-acid contained in muscle tissue and found in urine.1 A person may attempt to foil a drug test by drinking excessive amounts of water or diuretics such as herbal teas to flush the system. Creatinine and Specific Gravity are two ways to check for dilution and flushing, which are the most common mechanisms used to circumvent drug testing. Low Creatinine and Specific Gravity levels may indicate diluted urine. The absence of Creatinine (<5 mg/dL) is indicative of a specimen not consistent with human urine.
- Nitrite (NIT) tests for commonly used commercial adulterants. They work by oxidizing the major cannabinoid metabolite THC-COOH.2 Normal urine should contain no trace of Nitrites. Positive results generally indicate the presence of an adulterant.
- Glutaraldehyde (GLU) tests for the presence of aldehydes. Adulterants can contain Glutaraldehyde and can cause false negative screening results by disrupting the enzyme used in some immunoassay tests. Glutaraldehyde is not normally found in urine; therefore, detection of Glutaraldehyde in a urine specimen is generally indicates adulteration.
- pH tests for the presence of acidic or alkaline adulterants in urine. Normal pH levels should be in the range of 4.0 to 9.0. Values outside of this range may indicate that the specimen has been altered.
- Specific Gravity (SG) tests for specimen dilution. The normal range is from 1.003 to 1.030. Values outside this range may be the result of specimen dilution or adulteration.
- Oxidants/Pyridinium Chlorochromate (OXI/PCC) tests for the presence of oxidizing reagents such as bleach and hydrogen peroxide. Pyridinium Chlorochromate is a commonly used adulterant. Normal human urine should not contain Oxidants or PCC.
Additional information
| Product name | Adulteration Urine Test |
|---|---|
| Detection | Creatinine, Nitrite, Glutaraldehyde, Specific Gravity, Oxidants/Pyridinium Chlorochromate |
| Type | |
| Sample Type | |
| Pack Size | |
| Format | |
| Analyte Detection | |
| For Drug Test |