Categories
RSV Rapid Test
The Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) test is used to detect the presence of RSV in respiratory secretions, typically collected via a nasal swab or throat swab. RSV is a common virus that causes respiratory infections, especially in infants and young children. This test is to confirm RSV infections, enabling appropriate treatment and care for affected individuals, particularly during the RSV season in colder months.
Product information
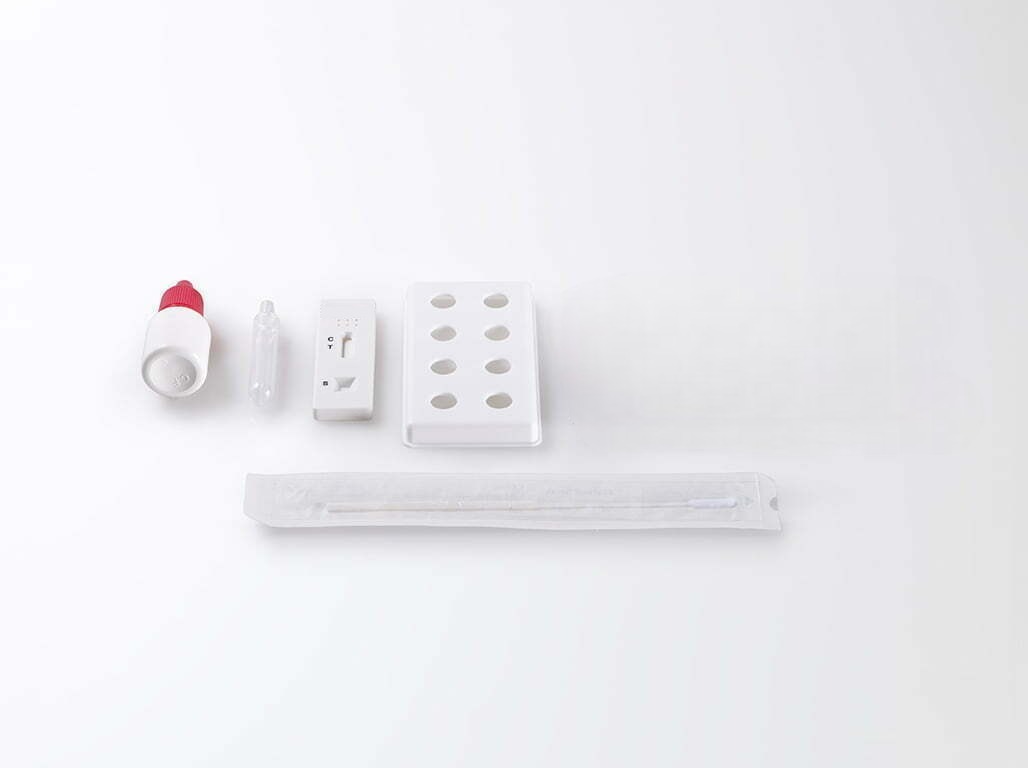
The RSV Rapid Test a lateral flow, qualitative immunochromatographic rapid test for the detection (respiratory syncytial virus) in the respiratory tract.
Advantages of RSV test
- Easy to perform
- No complex sample collection needed
- Accurate test result
General information
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is the most important cause of pneumonia and bronchiolitis in infants and small children. Like the other respiratory viruses, RSV causes a range of respiratory illness, the most common being a cold with profuse rhinorrhea. Between 1 and 2% of infected infants require hospitalization, the most severe disease occurring in the first year of life and in those with underlying cardiopulmonary disease.
In normal infants and children, the virus is shed for 2 to 3 weeks overall or 1 or 2 weeks after the children appear in the hospital. Because of its high infectivity and because hospital staff as well as patients are susceptible, RSV has emerged as the most frequent cause of nosocomial infections on pediatric wards.
The studies of Hall and Taber and their colleagues established that RSV bronchiolitis and pneumonia could be successfully treated by administration of ribavirin aerosol. This finding has made accurate, rapid identification of cases through laboratory methods an important part of the care of children in hospitals.
Contrary to the classical methods (Immunofluorescence and ELISA) which are laborious and time consuming, RSV Rapid Test is a fast, simple and highly sensitive test for the rapid and reliable detection of RSV in the respiratory tract.
The method employs a unique combination of monoclonal dye conjugate and polyclonal solid phase antibodies to selectively identify RSV with a high degree of sensitivity and specificity. After collection and treatment, the sample is added to the sample well (▷) of the reaction device. As the test sample flows through the absorbent device, the labelled antibody-dye conjugate binds to the RSV antigen (when present in the sample) forming an antibody antigen complex.
This complex binds to the polyclonal antibody in the positive reaction zone (T) producing a rose-pink colored band. In the absence of RSV, there is no line in the positive reaction zone (T). The reaction mixture continues flowing through the absorbent device, past the positive reaction zone (T) and control zone (C). Unbound conjugate binds to the reagent in the control zone producing a rose-pink colored band demonstrating that the reagents are functioning correctly.
Test procedure
- Bring all reagents at room temperature.
- Remove the test device from the pouch.
- Using the plastic pipette, add 5 drops (150 μL) of the extracted solution into the sample well.
- Read the results of the test 10 minutes after addition of the sample to the device.
Interpretation of the results
Negative result: One colored band appears in the control zone (C). No band is visible in the test zone (T).
Positive result: In addition to the control band (C), a clearly distinguishable band also appears in the test zone (T), indicating a positive result.
Invalid result: If there is no distinct colored band visible in both test and control windows, the test is inconclusive. Repeat the test.
| Product name | RSV Rapid Test |
|---|---|
| Detection | Respiratory Syncytial Virus in the respiratory tract |
| Type | Medical Rapid Test, Multi Panel Urine Test, Multi Pipet Urine Tests, Single Panel Urine Test |
| Sample Type | |
| Pack Size | |
| Format | |
| Analyte Detection |
Related products
-
Medical Tests
H. Pylori Antigen Rapid Test
Price requestThe Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) test is a diagnostic test used to detect the presence of H. pylori bacteria in the stomach lining. This bacterium can cause digestive issues, such as gastritis and peptic ulcers. The test is typically performed through breath, blood, or stool samples and is available through healthcare providers and diagnostic laboratories. It helps diagnose H. pylori infections, allowing for appropriate treatment and management to alleviate stomach-related health problems.
-
Medical Tests
Legionella Pneumophila Rapid Test
Price requestThe Legionella pneumophila test is a diagnostic test that specifically detects the Legionella pneumophila bacteria, a common cause of Legionnaires’ disease. This test is used to assess the presence of this pathogen in water sources, such as cooling towers and plumbing systems. It’s crucial for ensuring the safety of water systems in environments like hospitals, hotels, and industrial facilities.
-
Heart Markers
D-Dimer Rapid Test
Price requestThe D-dimer test is a test that measures the levels of D-dimer, a protein fragment, in the bloodstream. It’s a critical diagnostic tool for detecting abnormal blood clot formation, often associated with conditions like deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Healthcare providers use this test to assess the likelihood of clot-related disorders, aiding in diagnosis and guiding treatment decisions. It plays a crucial role in ensuring patient safety and timely medical interventions.
 Drug Test
Drug Test Heart Markers
Heart Markers Hormone Tests
Hormone Tests Medical Tests
Medical Tests Microbiology
Microbiology Parasite Infection
Parasite Infection Proteins and Inflammatory Markers
Proteins and Inflammatory Markers Qualitative Controls
Qualitative Controls Tumor Marker
Tumor Marker Viruses
Viruses